CODOS Update for Rabbit Ears Pass:
CODOS Update for Rabbit Ears Pass:
March 28, 2012
Summary |
Snowpack |
Melt Rate |
Stream Flows |
Forecast |
Previous Update |
pdf
Summary
Colorado’s substantially sub-par reservoir of SWE now contains two significant (D5 and D4) and one minor (D6) dust layers at/near the snowpack surface statewide, and is vulnerable to continued prolonged periods of dry, sunny weather combined with reduced snow albedo. This Update presents site-by-site and summary analyses of snowmelt rates at CODOS and other Snotel sites for Water Years 2006-2011.
Snowpack conditions on the Rabbit Ears Pass plateau are likely isothermal and releasing snowmelt runoff, with the possible exception of the very highest north-facing terrain. Merged dust layers D5/D4, and possibly D6, are reducing snow albedo throughout this locale and the Rabbit Ears Pass Snotel site has shown a recent decline in SWE. Should dry weather continue to dominate this spring season, and dust-enhanced snowmelt rates approach the average or maximum rates discussed below, snow all gone (SAG) may occur early at this Snotel site producing early peak streamflows, early passage of runoff center of mass, and steep descending limbs on local hydrographs.
SnowPack Discussion
We have no new first-hand snowpack observations to present. Our next visit to the Rabbit Ears Pass site will be in early April, as weather and dust conditions dictate.
Melt Rate
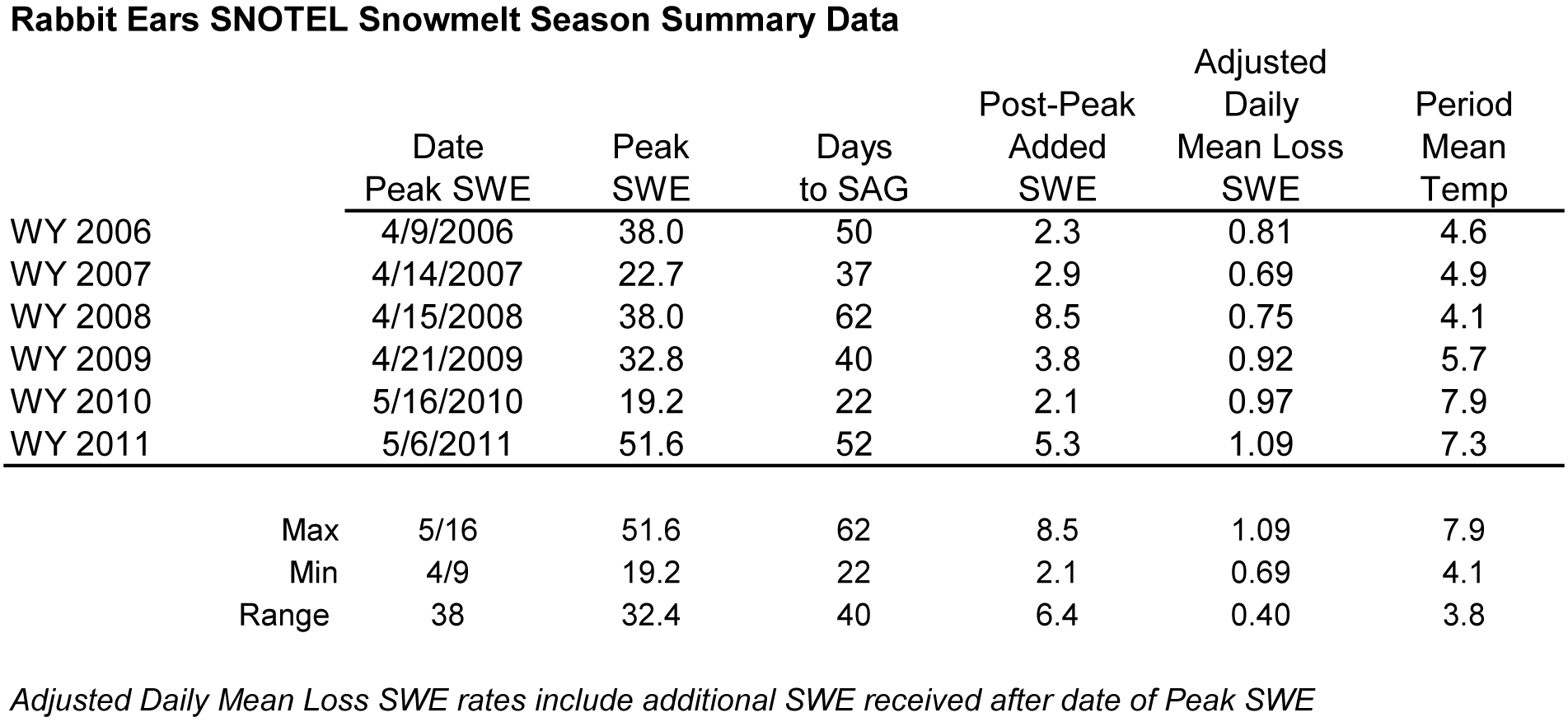
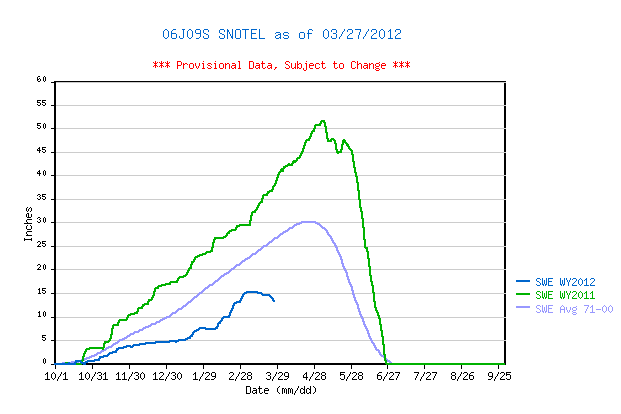
The table below presents Water Year analyses of snowmelt behavior at the Snotel station adjoining this CODOS site beginning with WY 2006. The date of Peak SWE and subsequent number of days to “snow all gone” (SAG) are shown for each Water Year. Then, the amount of additional SWE received after the date of Peak SWE is added to Peak SWE to calculate an “adjusted daily mean loss [of] SWE” rate during the snowmelt season that Year. Finally, the mean air temperature during the period from Peak SWE to SAG, as measured at the Snotel site, is shown for each Water Year. A current Snotel plot is presented below the table. The intent of this table is to refresh memories of snowmelt rates during the past several dust-influenced Spring seasons, and to assess this year’s snowpack conditions in light of those past years.
As of Tuesday, March 27, 2012, the Rabbit Ears Pass Snotel reports a loss of 1.1” SWE since March 21, a rate of 0.16” per day. This recent melt rate falls well short of the mean daily loss rates shown in the table below, and very far short of the maximum SWE loss rate last Spring of 1.94” per day, over a 5-day period ending June 7, 2011.
Stream Flows
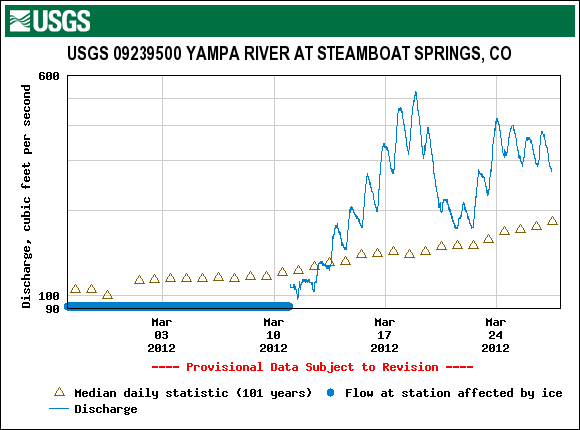
Streamflow data reflect a variety of processes influencing runoff rates, but recent data from the USGS Yampa River at Steamboat Springs stream gauge does include the influence of the reduction of snow albedo by D4 and very warm temperatures from March 10-17, a decline flows with restoration of higher snow albedo (with cooler weather) on March 18, and then another rapid increase in flows with the subsequent warmup and reduction in snow albedo as D5 emerged and merged with D4. Event D6 may also be contributing to the most recent data.
Forecast
As of Tuesday afternoon forecasters at the Grand Junction National Weather Service anticipate continued warm and generally dry weather through the remainder of this week, with the warmest temperatures of the week on Saturday. The northern mountains may experience some light showers and more cloudiness than the southern half of the state. Snowmelt rates are likely to continue to increase through Saturday.
By Saturday afternoon an approaching trough and associated cold front are expected to generate another episode of strong pre-frontal SW’ly winds for the State. Winds will sustain and become W’ly on Sunday. Dust source areas in the Colorado Plateau may yield to these SW’ly and W’ly winds and produce another dust event beginning Saturday afternoon. This weekend’s cold front may, once again, not deliver a significant winter storm. However, a return to cooler, more seasonable temperatures by Sunday/Monday does seem likely. In the absence of new snow with this weekend cold front, a dry D7 event, should it occur, would generally fall directly onto already exposed and merged D6/D5/D4 dust, further reducing snowpack albedo throughout the Colorado mountains.